What is a Fibroblast?
Fibroblasts are large, spindle-shaped cells found in our body. They are responsible for making the extracellular matrix and collagen. This connective-tissue is present throughout our body. It is important framework for our skin functioning and looking youthful.
The fibroblast growth factor (FGF) triggers a signal cascade. It activates our body to restore the processes that have diminished with aging.
Restoring Youth
For our skin to function properly, cell enzymes need to be activated. Then, followed by ATP production, which leads to changes in cellular function.
In addition, FGF plays an important role in anti-aging therapy as it is associated with the synthesis and activation of collagen and elastin, which are responsible for skin resistance and elasticity that decrease with aging.
Fibroblast Enhancing Treatments
Fibroblasts are cells that play a crucial role in the production of collagen, elastin, and other extracellular matrix components, which provide structural support to the skin and other tissues. In the realm of cosmetic medicine, "fibroblast treatments" often refer to non-surgical treatments using plasma energy to encourage skin tightening and rejuvenation.
Here are some types of treatments and procedures, including those that aim to stimulate fibroblasts or are related to their function:
-
Plasma Fibroblast Therapy
This non-invasive procedure utilizes a pen-like device that discharges a high-frequency electric current to small areas of the skin. The plasma tip doesn’t directly touch the skin, but instead releases a targeted current just above the skin. The energy produced creates small burns or "dots" that help in tightening the skin. This treatment can be used for eyelifts, wrinkle reduction, and the diminution of age spots and scarring. -
Microneedling
By using tiny needles to cause micro-injuries to the skin, microneedling stimulates the body's wound healing process, prompting the production of collagen and elastin. This leads to firmer, more youthful-looking skin. -
Radiofrequency (RF) Treatments
These treatments use radiofrequency energy to heat the deeper layers of the skin, stimulating fibroblast activity and promoting collagen production. -
Ultrasound Skin Tightening
Devices such as Ultherapy use focused ultrasound energy to target the deeper layers of the skin, boosting collagen production and resulting in skin tightening and lifting. -
Laser Resurfacing
Lasers can be used to remove the outer layers of the skin, stimulate collagen production in the underlying layers, and improve signs of aging. -
Dermal Fillers
While they don't directly stimulate fibroblasts, dermal fillers like hyaluronic acid can plump up the skin and reduce the appearance of wrinkles. Some research suggests that certain fillers might stimulate the body's production of collagen over time. -
Growth Factor Serums and Creams
Topical products containing growth factors can stimulate fibroblast activity, thereby promoting skin health and reducing signs of aging. -
Chemical Peels
By removing the top layers of the skin, chemical peels can boost collagen production and improve skin tone and texture.
When considering a facelift, eyelift, or any aesthetic procedure, it's crucial to consult with a board-certified dermatologist or plastic surgeon to discuss the most suitable treatment options and potential risks. Always ensure you're well-informed about the procedure, downtime, expected results, and potential side effects.
Understanding Fibroblasts: The Key to Youthful Skin
Our bodies are remarkable, intricate systems made up of various cells, each with its own unique role. Among these cells, there's a little-known hero called the fibroblast. Fibroblasts are the unsung champions of maintaining our skin's structure and youthfulness.
In this article, we'll delve into the world of fibroblasts, how they play a crucial role in keeping our skin looking vibrant, and explore natural ways to enhance their activity.
The Role of Fibroblasts
Fibroblasts are not your everyday cells; they're large, spindle-shaped cells that can be found throughout our bodies. Their primary responsibility is to create two essential components: the extracellular matrix and collagen. These components form the connective tissue that acts as a framework for our skin, providing the support and structure that keeps it looking youthful.
One of the key players in this process is the fibroblast growth factor (FGF). Think of FGF as a conductor in an orchestra. It sets off a signal cascade that activates our body to restore processes that may have dwindled with age. This signal cascade helps keep our skin functioning at its best.
Restoring Youthfulness
For our skin to function properly, it's vital to activate specific cell enzymes. Once these enzymes are activated, they kickstart ATP production, which leads to changes in cellular function. This cellular activity is crucial for maintaining the health and appearance of our skin.
FGF also plays a significant role in anti-aging therapy. It's associated with the synthesis and activation of collagen and elastin, which are two essential components responsible for the skin's resilience and elasticity. As we age, collagen and elastin production tends to decline, which can result in the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. FGF helps counteract these effects, contributing to a more youthful complexion.
Natural Ways to Enhance Fibroblast Activity
While FGF is a key player in maintaining youthful skin, there are natural ways to enhance fibroblast activity. These methods can help promote collagen production and improve the overall health of your skin.
-
Angelica Sinensis Extract: Research has shown that Angelica Sinensis extract can activate signaling pathways that enhance collagen production in skin fibroblasts. This natural extract can be a valuable addition to your skincare routine.
-
Green Tea Extract: Methanol extract from Camellia Sinensis, commonly known as green tea, has been shown to increase the proliferation of fibroblasts and collagen synthesis. Including green tea products in your skincare regimen can help boost fibroblast activity.
-
Turmeric and Curcumin: Curcumin, found in turmeric, promotes the proliferation of fibroblasts, aids in tissue formation, supports collagen deposition, and contributes to wound healing. Incorporating turmeric or curcumin into your diet or skincare routine can be beneficial.
-
Amniotic Fluid: Human amniotic fluid has been found to increase the viability and migration rate of human dermal fibroblasts. It enhances the expression of extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules like collagen, fibronectin, and elastin type III, which accelerates wound closure.
-
Natural Formation: Neovascularization, a process that occurs when fibroblasts proliferate and endothelial cells migrate to a wound area, can stimulate skin rejuvenation. This natural formation process is essential for maintaining healthy skin.
The Collagen Connection
Collagen, often referred to as the "glue" that holds our bodies together, plays a significant role in maintaining skin health. Various studies have explored the relationship between fibroblasts and collagen.
In the world of skincare, some treatments involve the use of electrical stimulation, microcurrents, plasma pen treatments, or lasers to boost fibroblast activity. These treatments aim to promote collagen production, thereby reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Collagen is like the scaffolding that supports your skin, and boosting its production can result in smoother, firmer skin.
The Impact of Oxygen
Oxygen also plays a role in the health of fibroblasts. It can influence the number of fibroblasts present in a particular area. While oxygen is necessary for fibroblast growth, too little of it can hinder their development and the formation of fibrotic tissue, potentially leading to scars.
The Complex Journey of Fibroblasts
Fibroblasts are not solitary workers; they collaborate with other cells and factors in the body to promote skin health. As inflammation approaches, macrophages and mast cells release fibroblast growth. These growth factors act as chemotactic agents, drawing fibroblasts to areas in need of repair. Phagocytes, another type of cell, release proteases that break down fibrotic tissue in adjacent areas. This process releases fibroblasts, allowing them to multiply and migrate further into the wound to aid in the healing process.
Angiogenesis and Blood Vessels
Angiogenesis is a fascinating process that occurs when fibroblasts proliferate and endothelial cells migrate to a wound area. This results in the formation of new blood vessels, which are essential for the nourishment and regeneration of the skin.
During the aging process, fibroblasts tend to increase in number, but their metabolic activity decreases. This change can lead to a reduction in the synthesis of crucial structural substances such as collagen, elastin, hyaluronic acid, and chondroitin. These substances are essential for maintaining the skin's elasticity, moisture, and overall youthful appearance.
The Role of Growth Factors
In the world of skin health, fibroblasts are also known for their ability to secrete growth factors. These growth factors serve as signals to attract epithelial cells to a wound site. Epithelial cells play a crucial role in wound healing and the regeneration of skin tissue. Growth factors are like beacons, guiding the necessary cells to where they are needed most.
Expression of Specific Proteins
The expression of specific proteins, like smooth muscle actin (SMA), can impact fibroblast contractility. In simple terms, SMA affects the ability of fibroblasts to contract and exert force. This property is essential for various skin functions.
Increasing the expression of SMA can enhance contractile activity, but it's not always mandatory for fibroblasts to exert force. Some cells can still generate force even with low levels of SMA expression. It's like having different gears in a car; even in low gear, you can still get things moving.
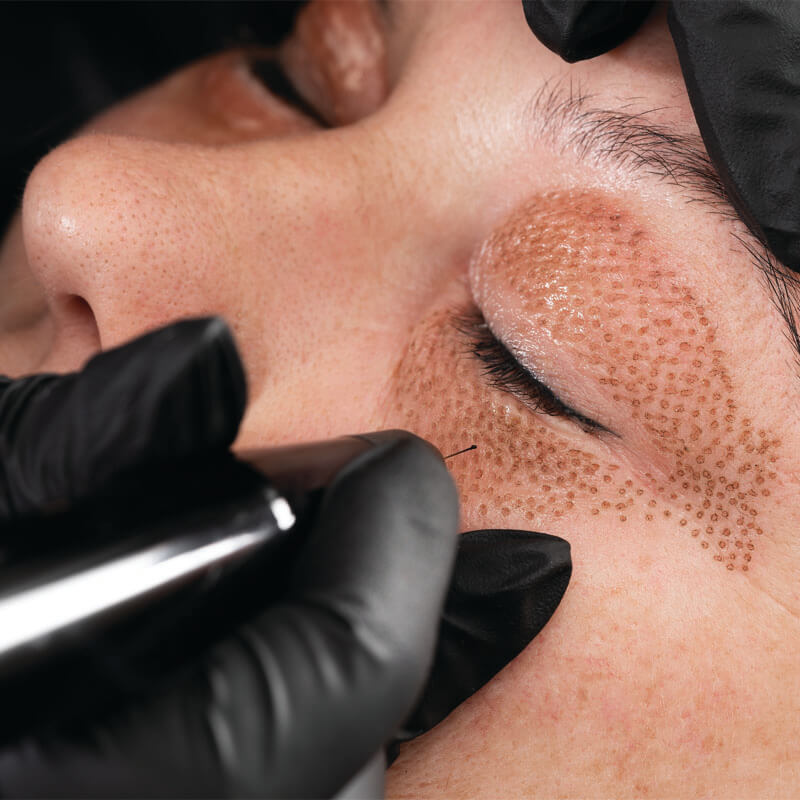
Plasma Pen Fibroblast Treatments
Fibroblasts are highly adaptable cells that can change their function by transforming into new cell types due to their location in the body.
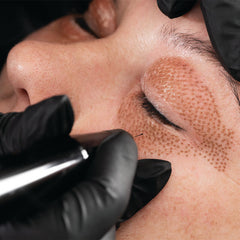
Giving energy by electrical stimulation such as microcurrent, plasma pen treatments, or lasers can improve fibroblast activity.
Is a non-surgical treatment using your a plasma pen. It's a natural way to tighten and lift while stimulating Fibroblasts. An electrical arc pulsed and skin shrink. This continual motion promotes firmness and youthful-looking skin.
In recent years, plasma fibroblast treatments have gained popularity as a non-surgical way to tighten and lift the skin while stimulating fibroblasts. These treatments utilize an electrical arc that pulsed and causes the skin to shrink. This continuous motion promotes firmness and a youthful appearance.
Plasma Fibroblast Treatment Costs for Facial Areas:
- Forehead: Includes Frown Lines - $400
- Frown Lines Alone: $250
- Upper Eyelids: $500
- Lower Eyelids: Comes with Crow's Feet treatment - $400
- Crow's Feet Only: $250
- Eyebrow Elevation: $250
- Laugh Lines (Nasolabial Folds): $400
- Upper Lip Area: $250
- Lower Lip Area: $250
- Contouring of Jaw & Under Chin: Addressing Double Chin & Jowls - $600
- Lines from Mouth to Chin (Marionette Lines): $400
Collagen XIV and Skin Health
Collagen XIV has been shown to have a significant impact on the differentiation of dermal fibroblasts and the synthesis of DNA in these cells. By reducing the differentiation and DNA synthesis of fibroblasts, collagen XIV helps maintain cell viability and stability. This ensures that fibroblasts continue to perform their crucial functions in supporting healthy skin.
The Role of Oxygen and TLR4
Oxygen levels play a vital role in fibroblast growth and function. Adequate oxygen is necessary for fibroblast growth and tissue repair. However, too little oxygen can inhibit fibroblast development and lead to the formation of fibrotic tissue, which can result in scarring.
Inhibition of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) has been reported to counteract certain fibrotic processes in different parts of the body. TLR4 activity in skin fibroblasts can affect skin subcutaneous tissue, which can contribute to fibrosis and other skin issues.
5 Notable Benefits of Plasma Pen Treatments
-
Non-Invasive Skin Tightening: Unlike surgical procedures, plasma pen fibroblast treatment offers a non-invasive alternative for tightening sagging or loose skin, making it a more attractive option for those hesitant about going under the knife.
-
Reduced Recovery Time: Compared to surgical procedures, the recovery time for plasma pen treatment is significantly shorter. While there might be some redness and small scabs in the treated area, these usually heal and fade within a week or two.
-
Natural Collagen Production: The treatment stimulates the body's natural healing response, leading to increased collagen and elastin production. This results in improved skin texture, firmness, and a more youthful appearance over time.
-
Versatility: Plasma pen fibroblast treatment can be used on various parts of the face and body. It's effective for addressing concerns like crow's feet, forehead lines, nasolabial folds, and even sagging skin on the neck or abdomen.
-
Cost-Effective: When compared to other rejuvenation procedures like surgical facelifts, the plasma pen fibroblast treatment tends to be more affordable, offering a cost-effective solution for those seeking noticeable skin improvement without the hefty price tag.
Fibroblasts are fascinating cells with a crucial role in maintaining the health and appearance of our skin. These versatile cells can adapt and transform to support various skin functions, from supporting collagen production to regenerating. Understanding the factors that influence fibroblast activity and discovering natural ways to enhance their function can contribute to healthier, more youthful-looking skin. Whether through the use of natural extracts or innovative treatments like plasma fibroblast therapy, harnessing the power of fibroblasts can be a key element in your journey to radiant skin.
Sources
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wound_healing
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1298129-overview
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/fibroblast
https://www.scielo.br/j/bjmbr/a/qnX3rMNFmBfPFVLsp5dVBvH/?lang=en
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0071660
https://stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13287-016-0303-6
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2014.00123/full
https://www.nature.com/articles/emm200996
https://www.molbiolcell.org/doi/10.1091/mbc.12.9.2730
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4779293/
https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/501145
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2019/2684108/